Wearable medical devices have become an essential part of modern healthcare recently. The designers of these new technologies aim to wear them on the body, continuously monitoring multiple health indicators. From measuring heart rate to detecting abnormal heart rhythms, wearable devices are revolutionizing the way people manage their health and how healthcare providers deliver care. These wearable devices provide real-time data, allowing you to take control of your health and detect problems before they arise. This approach differs from typical medical devices that are only used during doctor visits. The growing popularity of these devices signals a shift in healthcare toward personalized, convenient, and data-driven care, empowering individuals and supporting preventative care.
Smartwatches and Fitness Bands as Health Monitors
Fitness bands and smartwatches can do much more than just track steps and calories. Today, many of these devices are equipped with medical sensors that can monitor heart rate, blood oxygen levels, sleep patterns, and even atrial fibrillation. These devices continuously gather information, which smartphone apps can view or send to doctors. Some smartwatches can even perform an electrocardiogram (ECG) to detect irregular heart rhythms and send notifications if something is wrong. For people with heart problems or who want to keep their hearts healthy, these wearables are a user-friendly solution for staying informed about their body’s signals.
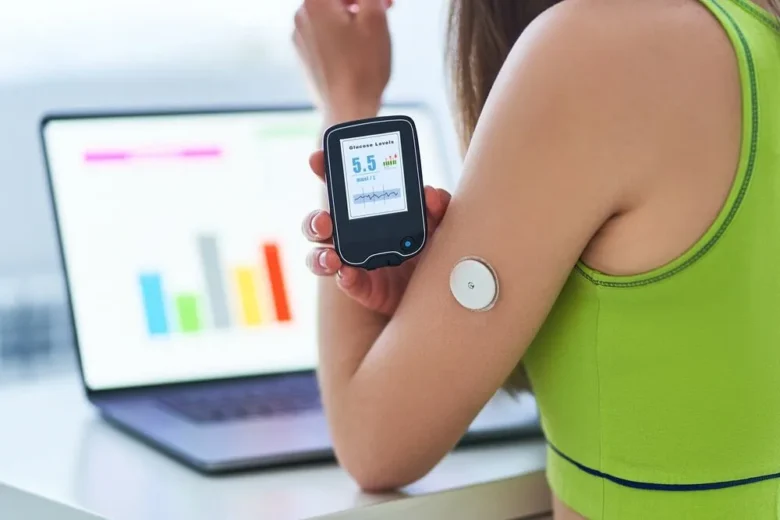
Continuous Glucose Monitors for Diabetes Management
People with diabetes must always work hard to keep their blood sugar levels under control. A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) makes this task easier and more effective. These devices are worn on the body, usually on the abdomen or arm, and measure blood sugar levels in real time via a small sensor implanted under the skin. The data is then sent to a smartphone or insulin pump to help users understand how their blood sugar levels change when they eat, exercise, or take medication. Some CGMs can also send notifications when blood sugar levels are too high or too low, reducing the risk of dangerous events. These devices help people with diabetes improve their quality of life by providing them with continuous and accurate information.
Smart Clothing and Biometric Patches
Wrist-worn devices are popular, but wearable medical technology has evolved into smart clothing and biometric patches. Sensors embedded in these clothes and patches can track indicators such as respiratory rate, muscle activity, hydration, and more. Smart clothing is often used in sports medicine and rehabilitation because it can provide a wealth of information about the body’s condition and recovery rate. Biometric patches are typically thin and adhesive and can track multiple measurements and send the data wirelessly to a mobile app or hospital system. These wearables are useful in hospitals because they allow doctors to monitor patients at all times without the need for large, bulky equipment. They also allow doctors to monitor patients’ recovery after they leave the hospital, which can reduce readmissions.
Wearable Heart and ECG Monitors
Wearable ECG devices provide important information to people who already have or are at risk for heart disease. These devices, such as chest straps, patches, or high-tech smartwatches, can record the heart’s electrical activity and detect irregular heart rhythms or other problems. Unlike standard ECG devices used in hospitals, these devices are portable and user-friendly. This makes it easier to collect data during daily activities. This feature allows doctors to detect symptoms that may not occur during a consultation. Some devices can even immediately alert the user and their doctor when they detect an abnormal heart rhythm that could be dangerous. Such detection allows them to respond more quickly and provide treatment.
New Ideas for Future Wearable Medical Devices
As technology advances, wearable medical devices are becoming more accurate, comfortable, and useful. Researchers are designing new wearables that can track more health information, such as hydration, body temperature, and potential early indicators of infection or illness. In the future, these devices could use artificial intelligence to provide real-time analyses and recommendations, doubling their value. There’s also a growing focus on making wearables more fashionable and unobtrusive, so more people can use them with confidence. Wearable technology in the medical field will make healthcare smarter, more connected, and more future-proof. It will help with everything from chronic disease management to health improvement and elder care.
Conclusion
Wearable medical devices are transforming healthcare, providing people with the tools they need to take charge of their health. These technologies can provide real-time information, continuously monitor your health, and offer personalized feedback to help you prevent, detect, and treat various health conditions. Wearable devices like smartwatches, blood glucose meters, biometric patches, and sleep monitors are making healthcare more accessible, convenient, and responsive. As more people use these devices in their daily lives, patient-centered, data-driven care will become increasingly valued. Both individuals and healthcare systems can benefit from wearable technology to improve outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance public health and education.
FAQs
1. Which medical devices can be worn?
Wearable medical devices are technologies that people can wear on their bodies to monitor their health, check vital signs, and provide real-time data to users and healthcare providers.
2. Are wearables suitable for medical use?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved many wearable medical devices, and they have been shown to provide accurate and reliable data when used correctly and kept up-to-date.
3. Can wearables replace a doctor’s visit?
Wearables are useful, but they are not a replacement for medical care. They can assist with continuous monitoring and prevention, but you should also see your doctor regularly.
4. Who can benefit from wearable medical devices?
Everyone can benefit from them, but they are especially helpful for people with chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, sleep problems, and high blood pressure.
5. What functions can a wearable blood glucose monitor perform?
A continuous glucose monitor has a small sensor implanted under the skin that measures blood sugar levels and sends real-time updates to a smartphone or insulin pump. This helps people with diabetes better manage their condition.